本文转载自:亦梦云烟博客
一. AXI DMA简介
AXI DMA IP核提供了AXI4内存之间或AXI4-Stream IP之间的内存直接访问,可选为分散收集工作模式,初始化,状态和管理寄存器等通过AXI4-Lite 从机几口访问,结构如图1所示,AXI DMA主要包括Memory Map和Stream两部分接口,前者连接PS段,后者连接带有流接口的PL IP核。

图1 AXI DMA结构框图
AXI DMA的特性如下:
1. AXI4协议
2. 支持 Scatter/Gather DMA
3. 直接寄存器模式
只需很少的FPGA资源就可以使用Scatter Gather引擎,在这种模式下,设置源地址(如MM2S)和目的地址(如S2MM),然后设置数据长度的寄存器。
4. AXI4支持多种数据位宽:32,64,128,256,512和1024位;
5. AXI4-Stream数据位宽支持:8,16,32,64,128,256,512和1024位;
6. 支持超过512字节重对齐。
1.1 开发环境
Windows 10 64位
Vivado 2018.2
XC7Z010-1-CLG400
1.2 例程简介
首先构建AXI DMA例程使用的硬件环境,在这个设计中,我们用DMA将内存中的数据传输到IP模块中,然后传输会内存,原则上这个IP模块可以是任意类型的数据产生模块,如ADC/DMA,在本例程中,我们使用FIFO来作为环路进行测试。如图2所示。
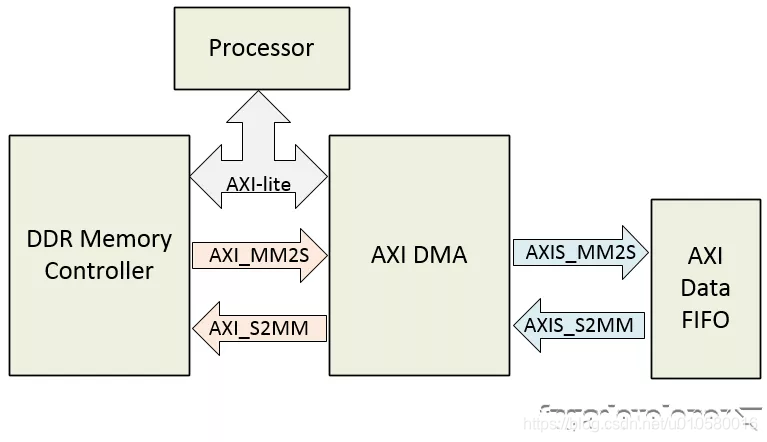
图2 本例程结构示意图
如图2所示,我们在PL中使用AXI DMA和AXI Data FIFO模块,AXI Lite总线用来配置AXI DMA,AXI_S2MM和AXI_MM2S用于内存和DMA控制器之间的通信。
2. 工程创建
2.1 添加AXI DMA
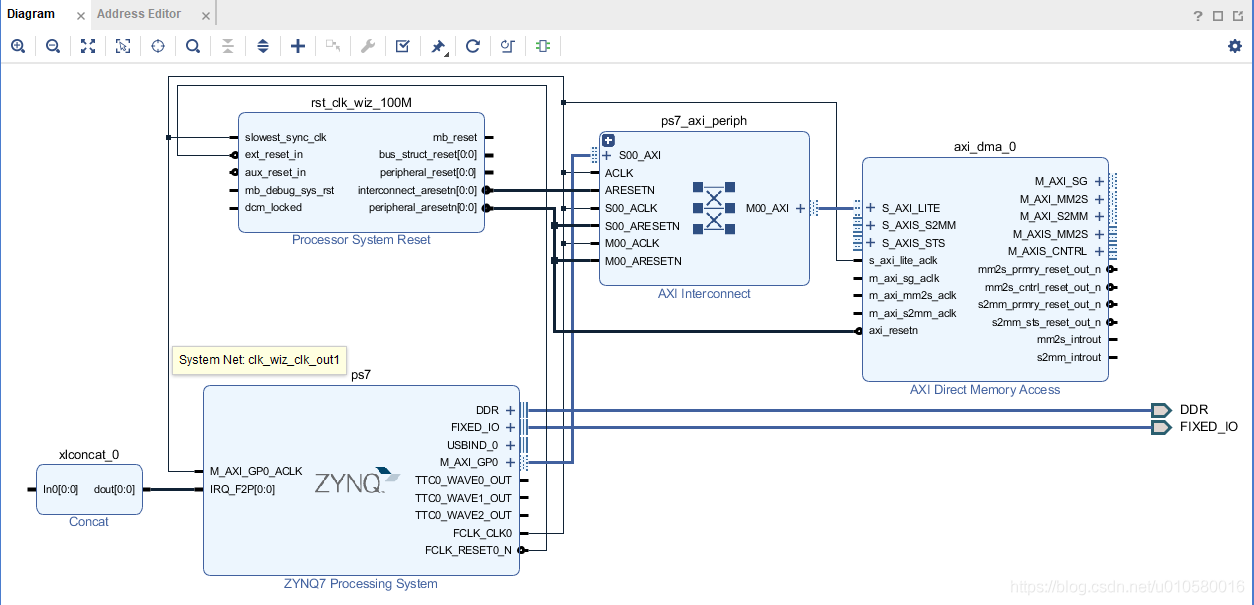
1. 打开Vivado模板工程,在Block Design中点击"Add IP",搜索AXI Direct Memory Access模块,双击添加到工程中。

2. 连接AXI总线。点击"Run Connection Automation",点击"OK",vivado会自动将AXI DMA连接到ZYNQ PS端,连接后如下图所示。
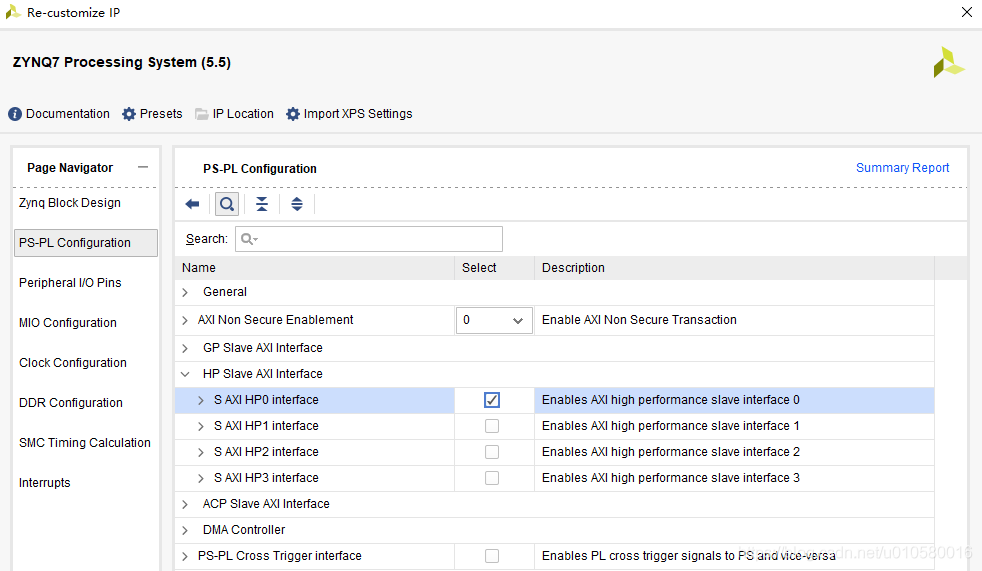
3. 现在,我们要连接AXI DMA控制器的M_AXI_SG, M_AXI_MM2S和M_AXI_S2MM到一个PS端的高性能AXI从机接口。模板工程中并没有这样的从机接口,所以,双击ZYNQ IP,配置该模块,选择PS-PL Configuration,勾选HP Slave AXI Interface > S AXI HP0 Interface,如下图所示。
4. 高性能AXI从机接口在模块原理图中显示如图,点击"Run Connection Automation",选择"processing_system7_0/S_AXI_HP0".
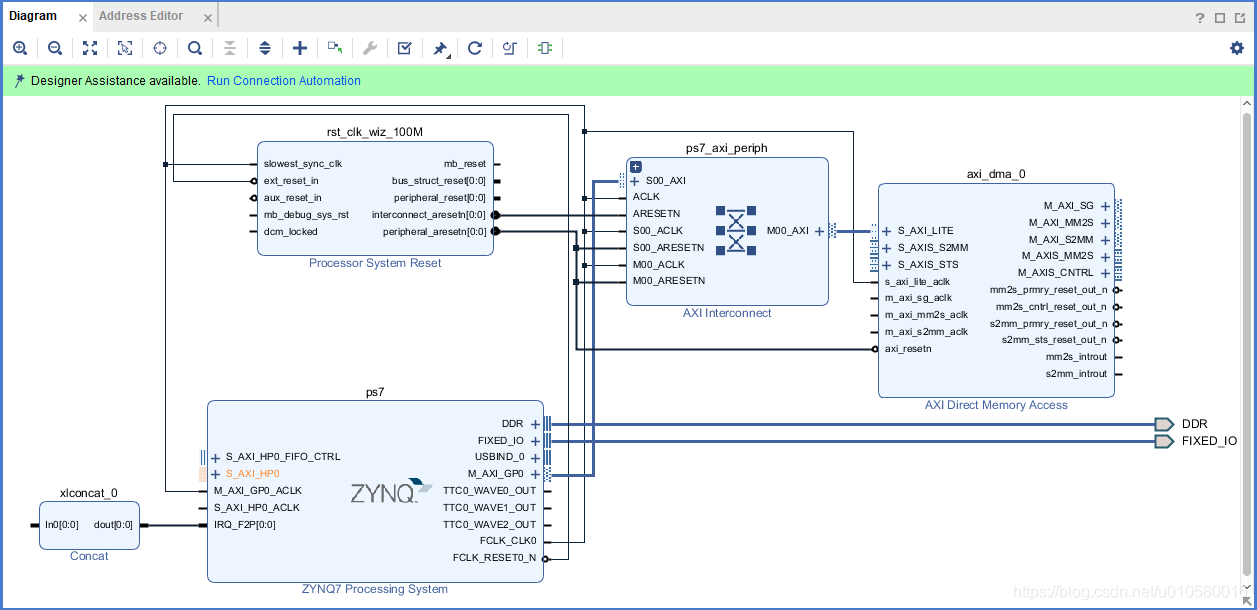

5. 此时,根据辅助设计提示,点击"Run Connection Automation",全选All Automation,默认即可。DMA连接完成后如下图所示。

6. 取消SG模式。双击axi_dma模块,取消"Enable Scatter Gather Engine"。配置如下
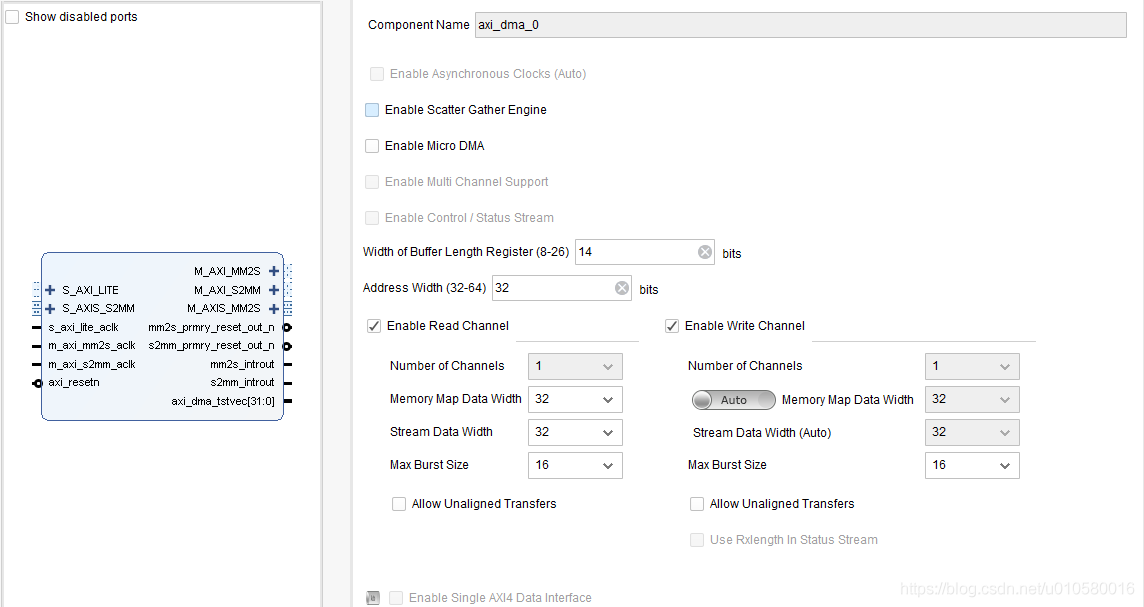
2.2 添加FIFO
1. 点击"Add IP",搜索"AXI-Stream Data FIFO".

2. 这里只能手动连接AXI总线。连接data FIFO的"S_AXIS"到AXI DMA的M_AXIS_MM2S。
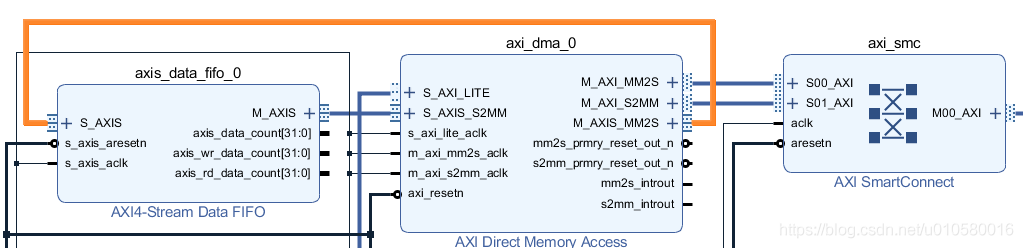
3. 连接data FIFO的“M_AXIS”到 AXI DMA的"S_AXIS_MM2S"。
4. data FIFO的s_axis_aresetn和s_axis_aclk到AXI DMA的axi_resetn和s_axi_lite_aclk。
5. 连接DMA中断到PS。 连接AXI DMA的mm2s_introut到xlconcat_0的In0,连接s2mm_introut到xlconcat_0的In1.
6. 点击Tools -> Validate Design,确认无误后最终原理图如下。
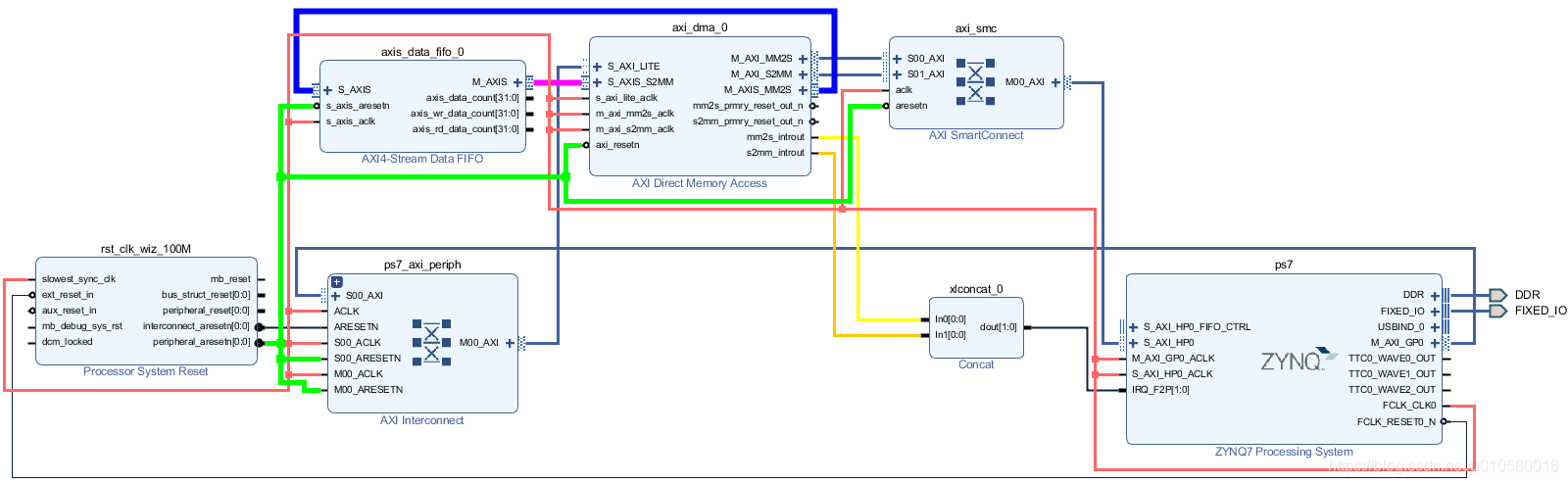
编译综合,生成bitstream,导出到SDK中进行软件设计。
3. SDK软件测试
1.1 创建SDK工程
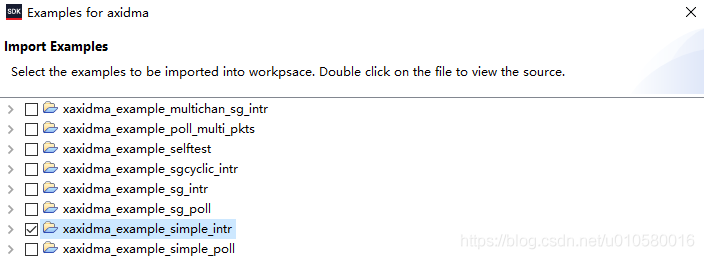
新建AXIDMA_bsp工程,在system.mss的Peripheral Drivers中,点击Import Examples,导入Xilinx官方例程。
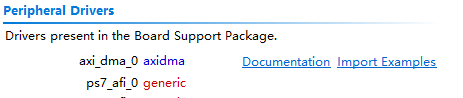
选择xaxidma_example_simple_intr例程。
1.2 编辑代码
dma_intr.h文件
#ifndef SRC_DMA_INTR_H_
#define SRC_DMA_INTR_H_
#include "xaxidma.h"
#include "xparameters.h"
#include "xil_exception.h"
#include "xdebug.h"
#include "xscugic.h"
/************************** Constant Definitions *****************************/
#define DMA_DEV_ID XPAR_AXIDMA_0_DEVICE_ID
#define MEM_BASE_ADDR 0x01000000
#define RX_INTR_ID XPAR_FABRIC_AXIDMA_0_S2MM_INTROUT_VEC_ID
#define TX_INTR_ID XPAR_FABRIC_AXIDMA_0_MM2S_INTROUT_VEC_ID
#define TX_BUFFER_BASE (MEM_BASE_ADDR + 0x00100000)
#define RX_BUFFER_BASE (MEM_BASE_ADDR + 0x00300000)
#define RX_BUFFER_HIGH (MEM_BASE_ADDR + 0x004FFFFF)
#define INTC_DEVICE_ID XPAR_SCUGIC_SINGLE_DEVICE_ID
#define INTC XScuGic
#define INTC_HANDLER XScuGic_InterruptHandler
/* Timeout loop counter for reset
*/
#define RESET_TIMEOUT_COUNTER 10000
#define TEST_START_VALUE 0xC
/*
* Buffer and Buffer Descriptor related constant definition
*/
#define MAX_PKT_LEN 0x100
#define NUMBER_OF_TRANSFERS 10
/*
* Flags interrupt handlers use to notify the application context the events.
*/
extern volatile int TxDone;
extern volatile int RxDone;
extern volatile int Error;
int SetupIntrSystem(INTC * IntcInstancePtr,
XAxiDma * AxiDmaPtr, u16 TxIntrId, u16 RxIntrId);
void DisableIntrSystem(INTC * IntcInstancePtr,
u16 TxIntrId, u16 RxIntrId);
/************************** Function Prototypes ******************************/
int CheckData(int Length, u8 StartValue);
void TxIntrHandler(void *Callback);
void RxIntrHandler(void *Callback);
#endif /* SRC_DMA_INTR_H_ */
dma_intr.c
#include "dma_intr.h"
/*
* Flags interrupt handlers use to notify the application context the events.
*/
volatile int TxDone;
volatile int RxDone;
volatile int Error;
/*****************************************************************************/
/*
*
* This function checks data buffer after the DMA transfer is finished.
*
* We use the static tx/rx buffers.
*
* @param Length is the length to check
* @param StartValue is the starting value of the first byte
*
* @return
* - XST_SUCCESS if validation is successful
* - XST_FAILURE if validation is failure.
*
* @note None.
*
******************************************************************************/
int CheckData(int Length, u8 StartValue)
{
u8 *RxPacket;
int Index = 0;
u8 Value;
RxPacket = (u8 *) RX_BUFFER_BASE;
Value = StartValue;
/* Invalidate the DestBuffer before receiving the data, in case the
* Data Cache is enabled
*/
#ifndef __aarch64__
Xil_DCacheInvalidateRange((UINTPTR)RxPacket, Length);
#endif
for(Index = 0; Index < Length; Index++) {
if (RxPacket[Index] != Value) {
xil_printf("Data error %d: %x/%x\r\n",
Index, RxPacket[Index], Value);
return XST_FAILURE;
}
Value = (Value + 1) & 0xFF;
}
return XST_SUCCESS;
}
/*****************************************************************************/
/*
*
* This is the DMA TX Interrupt handler function.
*
* It gets the interrupt status from the hardware, acknowledges it, and if any
* error happens, it resets the hardware. Otherwise, if a completion interrupt
* is present, then sets the TxDone.flag
*
* @param Callback is a pointer to TX channel of the DMA engine.
*
* @return None.
*
* @note None.
*
******************************************************************************/
void TxIntrHandler(void *Callback)
{
u32 IrqStatus;
int TimeOut;
XAxiDma *AxiDmaInst = (XAxiDma *)Callback;
/* Read pending interrupts */
IrqStatus = XAxiDma_IntrGetIrq(AxiDmaInst, XAXIDMA_DMA_TO_DEVICE);
/* Acknowledge pending interrupts */
XAxiDma_IntrAckIrq(AxiDmaInst, IrqStatus, XAXIDMA_DMA_TO_DEVICE);
/*
* If no interrupt is asserted, we do not do anything
*/
if (!(IrqStatus & XAXIDMA_IRQ_ALL_MASK)) {
return;
}
/*
* If error interrupt is asserted, raise error flag, reset the
* hardware to recover from the error, and return with no further
* processing.
*/
if ((IrqStatus & XAXIDMA_IRQ_ERROR_MASK)) {
Error = 1;
/*
* Reset should never fail for transmit channel
*/
XAxiDma_Reset(AxiDmaInst);
TimeOut = RESET_TIMEOUT_COUNTER;
while (TimeOut) {
if (XAxiDma_ResetIsDone(AxiDmaInst)) {
break;
}
TimeOut -= 1;
}
return;
}
/*
* If Completion interrupt is asserted, then set the TxDone flag
*/
if ((IrqStatus & XAXIDMA_IRQ_IOC_MASK)) {
TxDone = 1;
}
}
/*****************************************************************************/
/*
*
* This is the DMA RX interrupt handler function
*
* It gets the interrupt status from the hardware, acknowledges it, and if any
* error happens, it resets the hardware. Otherwise, if a completion interrupt
* is present, then it sets the RxDone flag.
*
* @param Callback is a pointer to RX channel of the DMA engine.
*
* @return None.
*
* @note None.
*
******************************************************************************/
void RxIntrHandler(void *Callback)
{
u32 IrqStatus;
int TimeOut;
XAxiDma *AxiDmaInst = (XAxiDma *)Callback;
/* Read pending interrupts */
IrqStatus = XAxiDma_IntrGetIrq(AxiDmaInst, XAXIDMA_DEVICE_TO_DMA);
/* Acknowledge pending interrupts */
XAxiDma_IntrAckIrq(AxiDmaInst, IrqStatus, XAXIDMA_DEVICE_TO_DMA);
/*
* If no interrupt is asserted, we do not do anything
*/
if (!(IrqStatus & XAXIDMA_IRQ_ALL_MASK)) {
return;
}
/*
* If error interrupt is asserted, raise error flag, reset the
* hardware to recover from the error, and return with no further
* processing.
*/
if ((IrqStatus & XAXIDMA_IRQ_ERROR_MASK)) {
Error = 1;
/* Reset could fail and hang
* NEED a way to handle this or do not call it??
*/
XAxiDma_Reset(AxiDmaInst);
TimeOut = RESET_TIMEOUT_COUNTER;
while (TimeOut) {
if(XAxiDma_ResetIsDone(AxiDmaInst)) {
break;
}
TimeOut -= 1;
}
return;
}
/*
* If completion interrupt is asserted, then set RxDone flag
*/
if ((IrqStatus & XAXIDMA_IRQ_IOC_MASK)) {
RxDone = 1;
}
}
/*****************************************************************************/
/*
*
* This function setups the interrupt system so interrupts can occur for the
* DMA, it assumes INTC component exists in the hardware system.
*
* @param IntcInstancePtr is a pointer to the instance of the INTC.
* @param AxiDmaPtr is a pointer to the instance of the DMA engine
* @param TxIntrId is the TX channel Interrupt ID.
* @param RxIntrId is the RX channel Interrupt ID.
*
* @return
* - XST_SUCCESS if successful,
* - XST_FAILURE.if not succesful
*
* @note None.
*
******************************************************************************/
int SetupIntrSystem(INTC * IntcInstancePtr,
XAxiDma * AxiDmaPtr, u16 TxIntrId, u16 RxIntrId)
{
int Status;
XScuGic_Config *IntcConfig;
/*
* Initialize the interrupt controller driver so that it is ready to
* use.
*/
IntcConfig = XScuGic_LookupConfig(INTC_DEVICE_ID);
if (NULL == IntcConfig) {
return XST_FAILURE;
}
Status = XScuGic_CfgInitialize(IntcInstancePtr, IntcConfig,
IntcConfig->CpuBaseAddress);
if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
return XST_FAILURE;
}
XScuGic_SetPriorityTriggerType(IntcInstancePtr, TxIntrId, 0xA0, 0x3);
XScuGic_SetPriorityTriggerType(IntcInstancePtr, RxIntrId, 0xA0, 0x3);
/*
* Connect the device driver handler that will be called when an
* interrupt for the device occurs, the handler defined above performs
* the specific interrupt processing for the device.
*/
Status = XScuGic_Connect(IntcInstancePtr, TxIntrId,
(Xil_InterruptHandler)TxIntrHandler,
AxiDmaPtr);
if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
return Status;
}
Status = XScuGic_Connect(IntcInstancePtr, RxIntrId,
(Xil_InterruptHandler)RxIntrHandler,
AxiDmaPtr);
if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
return Status;
}
XScuGic_Enable(IntcInstancePtr, TxIntrId);
XScuGic_Enable(IntcInstancePtr, RxIntrId);
/* Enable interrupts from the hardware */
Xil_ExceptionInit();
Xil_ExceptionRegisterHandler(XIL_EXCEPTION_ID_INT,
(Xil_ExceptionHandler)INTC_HANDLER,
(void *)IntcInstancePtr);
Xil_ExceptionEnable();
return XST_SUCCESS;
}
/*****************************************************************************/
/**
*
* This function disables the interrupts for DMA engine.
*
* @param IntcInstancePtr is the pointer to the INTC component instance
* @param TxIntrId is interrupt ID associated w/ DMA TX channel
* @param RxIntrId is interrupt ID associated w/ DMA RX channel
*
* @return None.
*
* @note None.
*
******************************************************************************/
void DisableIntrSystem(INTC * IntcInstancePtr,
u16 TxIntrId, u16 RxIntrId)
{
XScuGic_Disconnect(IntcInstancePtr, TxIntrId);
XScuGic_Disconnect(IntcInstancePtr, RxIntrId);
}
main.c文件
#include "xaxidma.h"
#include "xparameters.h"
#include "xil_exception.h"
#include "xdebug.h"
#include "xscugic.h"
#include "dma_intr.h"
static XAxiDma AxiDma; /* Instance of the XAxiDma */
static INTC Intc; /* Instance of the Interrupt Controller */
/*****************************************************************************/
/**
*
* Main function
*
* This function is the main entry of the interrupt test. It does the following:
* Initialize the DMA engine
* Set up Tx and Rx channels
* Set up the interrupt system for the Tx and Rx interrupts
* Submit a transfer
* Wait for the transfer to finish
* Check transfer status
* Disable Tx and Rx interrupts
* Print test status and exit
*
* @param None
*
* @return
* - XST_SUCCESS if example finishes successfully
* - XST_FAILURE if example fails.
*
* @note None.
*
******************************************************************************/
int axi_dma_test()
{
int Status;
XAxiDma_Config *Config;
int Tries = NUMBER_OF_TRANSFERS;
int Index;
u8 *TxBufferPtr;
u8 *RxBufferPtr;
u8 Value;
TxBufferPtr = (u8 *)TX_BUFFER_BASE ;
RxBufferPtr = (u8 *)RX_BUFFER_BASE;
xil_printf("\r\n--- Entering main() --- \r\n");
Config = XAxiDma_LookupConfig(DMA_DEV_ID);
if (!Config) {
xil_printf("No config found for %d\r\n", DMA_DEV_ID);
return XST_FAILURE;
}
/* Initialize DMA engine */
Status = XAxiDma_CfgInitialize(&AxiDma, Config);
if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
xil_printf("Initialization failed %d\r\n", Status);
return XST_FAILURE;
}
if(XAxiDma_HasSg(&AxiDma)){
xil_printf("Device configured as SG mode \r\n");
return XST_FAILURE;
}
/* Set up Interrupt system */
Status = SetupIntrSystem(&Intc, &AxiDma, TX_INTR_ID, RX_INTR_ID);
if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
xil_printf("Failed intr setup\r\n");
return XST_FAILURE;
}
/* Disable all interrupts before setup */
XAxiDma_IntrDisable(&AxiDma, XAXIDMA_IRQ_ALL_MASK,
XAXIDMA_DMA_TO_DEVICE);
XAxiDma_IntrDisable(&AxiDma, XAXIDMA_IRQ_ALL_MASK,
XAXIDMA_DEVICE_TO_DMA);
/* Enable all interrupts */
XAxiDma_IntrEnable(&AxiDma, XAXIDMA_IRQ_ALL_MASK,
XAXIDMA_DMA_TO_DEVICE);
XAxiDma_IntrEnable(&AxiDma, XAXIDMA_IRQ_ALL_MASK,
XAXIDMA_DEVICE_TO_DMA);
/* Initialize flags before start transfer test */
TxDone = 0;
RxDone = 0;
Error = 0;
Value = TEST_START_VALUE;
for(Index = 0; Index < MAX_PKT_LEN; Index ++) {
TxBufferPtr[Index] = Value;
Value = (Value + 1) & 0xFF;
}
/* Flush the SrcBuffer before the DMA transfer, in case the Data Cache
* is enabled
*/
Xil_DCacheFlushRange((UINTPTR)TxBufferPtr, MAX_PKT_LEN);
#ifdef __aarch64__
Xil_DCacheFlushRange((UINTPTR)RxBufferPtr, MAX_PKT_LEN);
#endif
/* Send a packet */
for(Index = 0; Index < Tries; Index ++) {
Status = XAxiDma_SimpleTransfer(&AxiDma,(UINTPTR) RxBufferPtr,
MAX_PKT_LEN, XAXIDMA_DEVICE_TO_DMA);
if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
return XST_FAILURE;
}
Status = XAxiDma_SimpleTransfer(&AxiDma,(UINTPTR) TxBufferPtr,
MAX_PKT_LEN, XAXIDMA_DMA_TO_DEVICE);
if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
return XST_FAILURE;
}
/*
* Wait TX done and RX done
*/
while (!TxDone && !RxDone && !Error) {
/* NOP */
}
if (Error) {
xil_printf("Failed test transmit%s done, "
"receive%s done\r\n", TxDone? "":" not",
RxDone? "":" not");
goto Done;
}
/*
* Test finished, check data
*/
Status = CheckData(MAX_PKT_LEN, 0xC);
if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
xil_printf("Data check failed\r\n");
goto Done;
}
}
xil_printf("Successfully ran AXI DMA interrupt Example\r\n");
/* Disable TX and RX Ring interrupts and return success */
DisableIntrSystem(&Intc, TX_INTR_ID, RX_INTR_ID);
Done:
xil_printf("--- Exiting main() --- \r\n");
return XST_SUCCESS;
}
int main(void)
{
axi_dma_test();
return XST_SUCCESS;
}
1.3 编译调试。
下载bitstream文件后,运行app程序,在终端中显示如下。

通过断点调试观察内存状态。
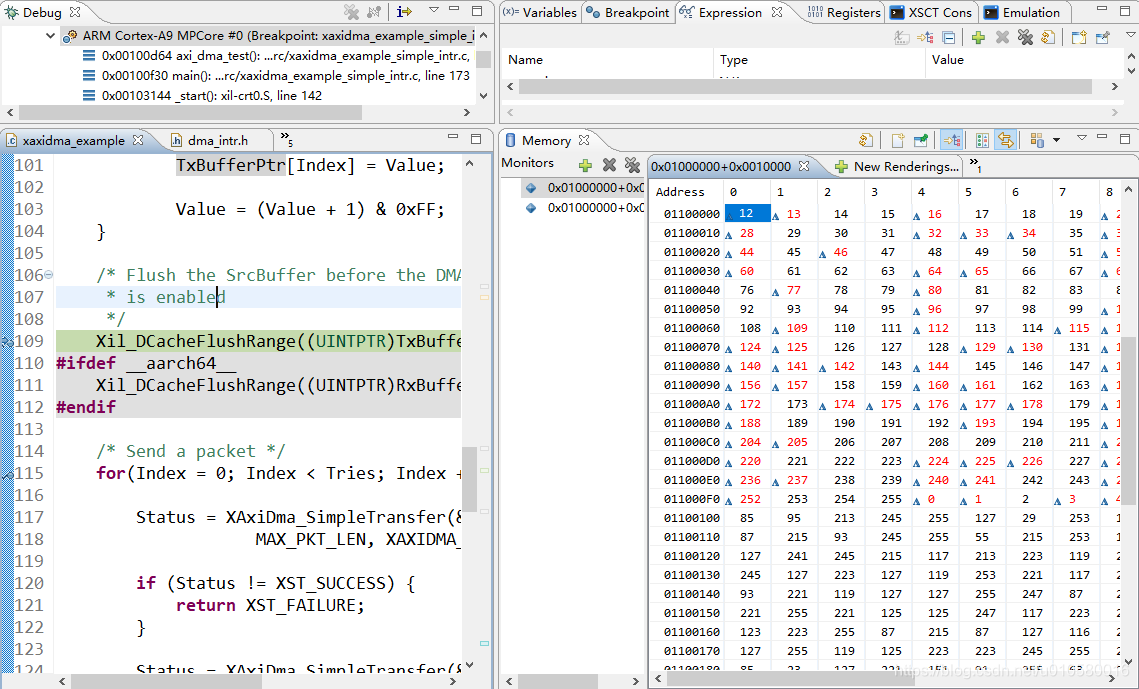
在数据发送前,先赋值发送数据包,此时发送数据为0~255而接收数据位无效数据。
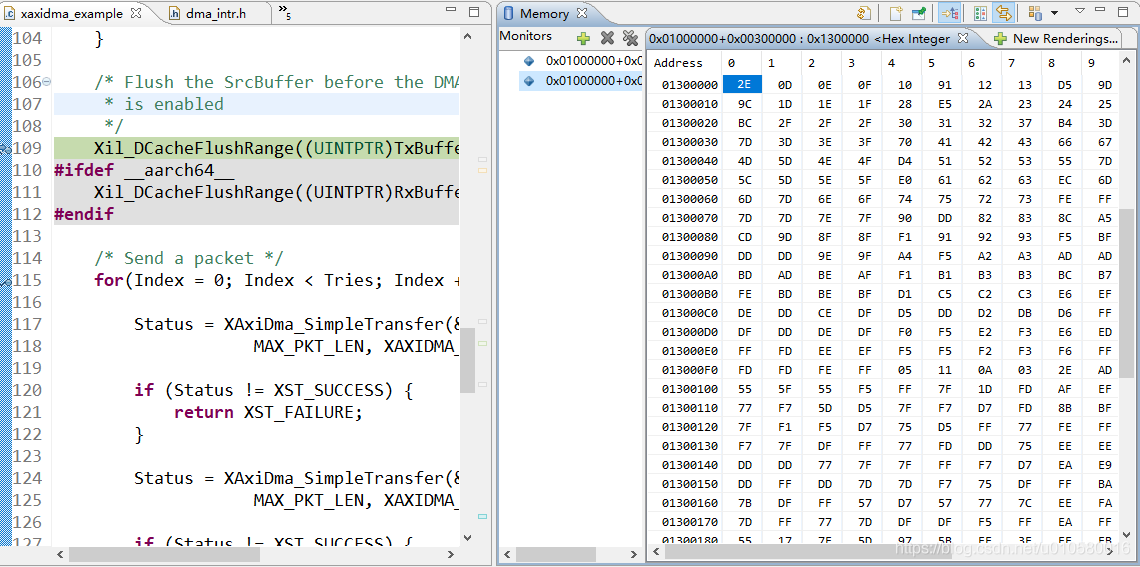
在下面位置打断点,观察接收数据内存数据。

可以看到接收的数据与发送的数据一致。
4 Linux驱动AXI DMA
4.1 安装devicetree生成工具
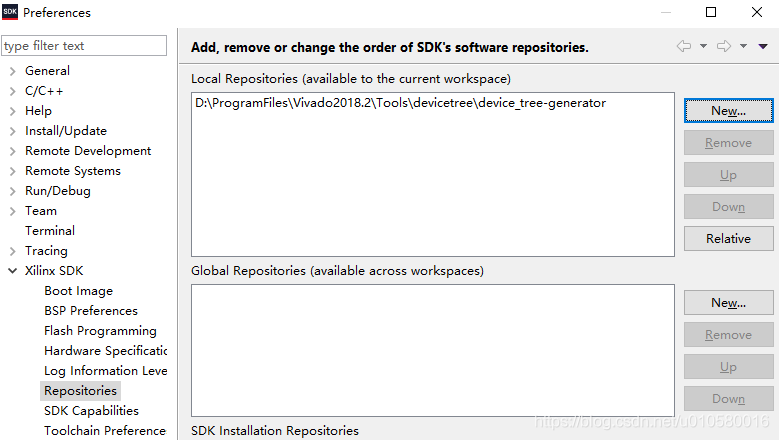
在Vvivado安装目录下创建一个空文件夹,这里命名为Tools/devicetree,用git下载device_tree-generator。
git clone https://github.com/Xilinx/device-tree-xlnx.git device_tree-generator
在Xilinx SDK软件中,点击Xilinx-> Repositories,在Local Repositories添加上面的路径。
4.2 创建设备树文件
创建BSP工程,点击File -> New -> Board Support Package, 在Board Support Package框中选择device_tree.
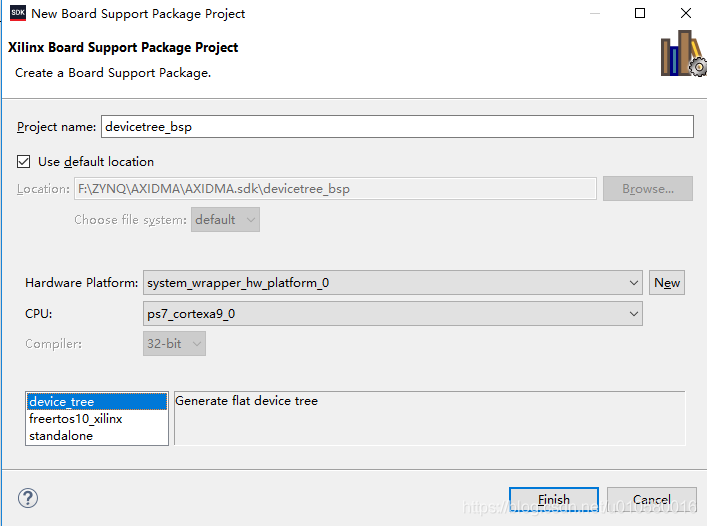
在bootargs中输入:console=ttyPS0,115200 root=/dev/mmcblk0p2 rw rootfstype=ext4 earlyprintk rootwait
此时,创建的工程中pl.dtsi是PL侧的设备树信息。
打开pl.dtsi内容如下,可以看到axi_dma添加了两个通道,一个读和一个写通道。
/ {
amba_pl: amba_pl {
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <1>;
compatible = "simple-bus";
ranges ;
axi_dma_0: dma@40400000 {
#dma-cells = <1>;
clock-names = "s_axi_lite_aclk", "m_axi_mm2s_aclk", "m_axi_s2mm_aclk";
clocks = <&clkc 15>, <&clkc 15>, <&clkc 15>;
compatible = "xlnx,axi-dma-7.1", "xlnx,axi-dma-1.00.a";
interrupt-names = "mm2s_introut", "s2mm_introut";
interrupt-parent = <&intc>;
interrupts = <0 29 4 0 30 4>;
reg = <0x40400000 0x10000>;
xlnx,addrwidth = <0x20>;
xlnx,sg-length-width = <0xe>;
dma-channel@40400000 {
compatible = "xlnx,axi-dma-mm2s-channel";
dma-channels = <0x1>;
interrupts = <0 29 4>;
xlnx,datawidth = <0x20>;
xlnx,device-id = <0x0>;
};
dma-channel@40400030 {
compatible = "xlnx,axi-dma-s2mm-channel";
dma-channels = <0x1>;
interrupts = <0 30 4>;
xlnx,datawidth = <0x20>;
xlnx,device-id = <0x0>;
};
};
};
};
制作BOOT.bin启动镜像。
4.3 编译Linux系统文件
配置Linux内核使其支持AXI DMA。在linux kernel根目录下执行:
# make menuconfig
选择Device Drivers > DMA Engine support > Xilinx DMA Engines --->
勾选Xilinx AXI DMA Engine。

编辑设备树文件:pl.dtsi文件中添加以下内容。
axidma_chrdev: axidma_chrdev@0 {
compatible = "xlnx,axidma-chrdev";
dmas = <&axi_dma_0 0 &axi_dma_0 1>;
dma-names = "tx_channel", "rx_channel";
};
将devicetree工程中的设备树源文件复制到Ubuntu中。
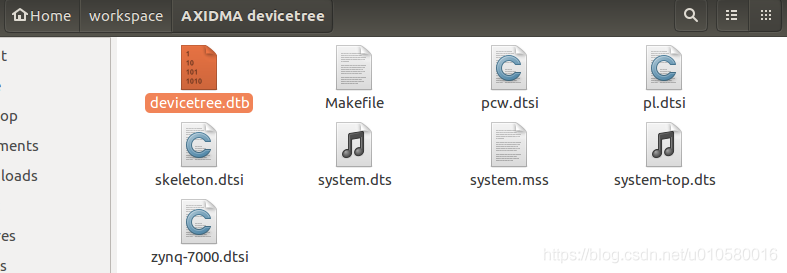
编译设备树:
# ./scripts/dtc/dtc -I dts -O dtb -o /home/biac/workspace/AXIDMA\
devicetree/devicetree.dtb /home/biac/workspace/AXIDMA\ devicetree/system-top.dts
其中./scripts/dtc/dtc为Zturn board Linux内核目录下的文件,终端在该目录下打开。
将本文生成的以下文件复制到SD卡中,启动Linux系统。
BOOT.bin, devicetree.dtb, 7z010.bit
参考资料
[1] http://www.fpgadeveloper.com/2014/08/using-the-axi-dma-in-vivado.html